

It is the most straightforward setup with a single click. This setup is geared for those who are already working with Docker and Docker Compose. Developed by Kubernetes, it has the broadest support of all three operating systems – Windows, MacOS, and Linux.ĭocker Desktop for Mac/Windows now ships with a bundled Kubernetes.

With that caveat, let’s jump into Kubernetes. These single-node installations are not recommended for production deployment. In this article, we are going to go over all the different options that make it easier-than-before to run Kubernetes on your local computer for development. With a simple one-line command, Ubuntu users can instantly deploy a K8s appliance.Īnd when it comes down to running Kubernetes in production, in the early 2019, Gravitational has released a radically simple way to create and manage Kuberntetes clusters, which is based on immutable cluster image files instead of traditional way of relying on configuration files.
Docker desktop kubernetes vs minikube install#
Later, in December of 2018, Canonical announced a snap package of the MicroK8s install package for the widespread Ubuntu distribution. With a few UI clicks, Docker users were able to deploy a single node cluster development environment. In July of 2018, Docker added Kubernetes into the Docker Desktop for both Mac and Windows Desktop. Today, there are many options for users looking to explore Kubernetes. Three years ago, Kubernetes released Minikube, a standalone tool that runs a single node cluster inside a Virtual Machine (VM) which allowed users to explore and try out Kubernetes on their local laptops. These new developments now make it easier for users to evaluate, play, and test Kubernetes.
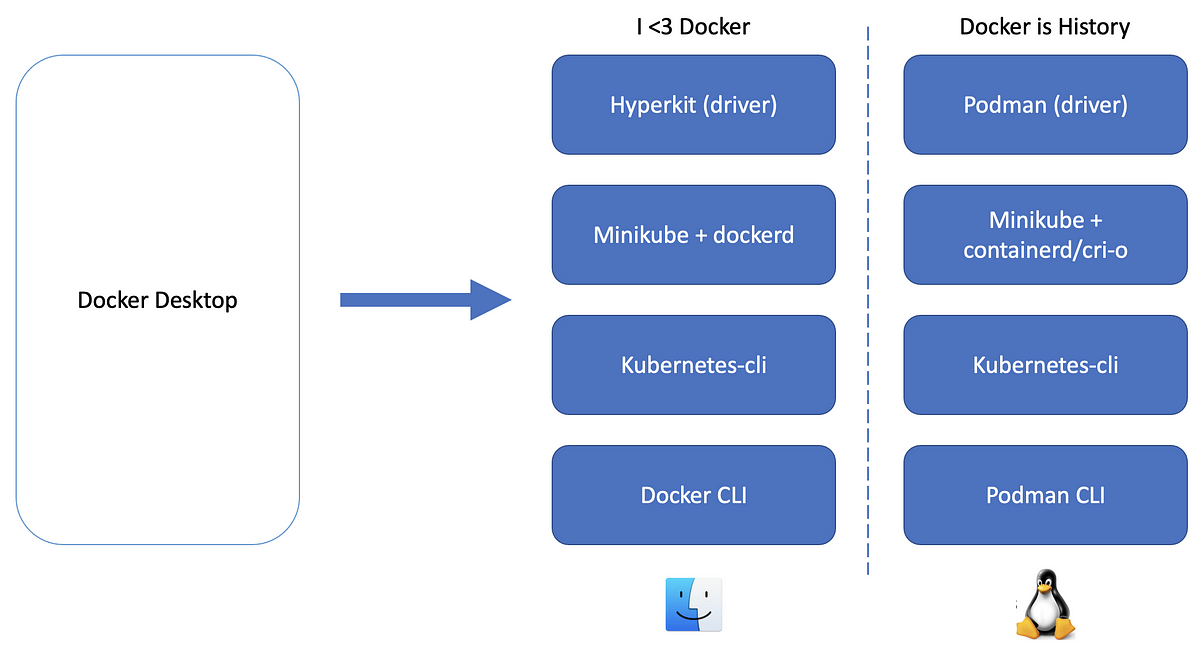
But with recent developments in the Kubernetes space, users now have more options to explore and run Kubernetes on their local machines. However, setting up a Kubernetes cluster is challenging even for the most technical users.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
